To search for strings, select Search For Strings... This will bring up the String Search Dialog
where you can configure the search criteria before initiating the search.
For Strings... This will bring up the String Search Dialog
where you can configure the search criteria before initiating the search.
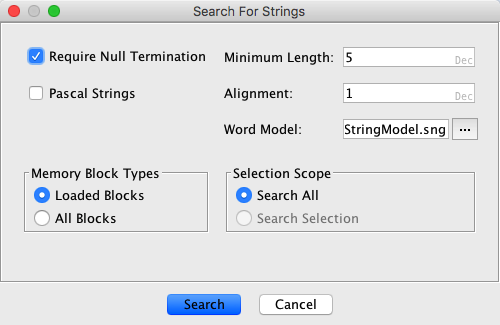
Search for Strings searches the entire program or a specific selection for possible Ascii or Unicode strings from the main menu. The results will be displayed in a table that can be filtered and sorted and provides actions for creating strings.
To search for strings, select Search
For Strings... This will bring up the String Search Dialog where you can configure the search criteria before initiating the search.
- Minimum Length - determines the shortest length of possible strings to display.
- Alignment - indicates the search should only return results that start at an address with the indicated byte alignment.
- Require Null Termination - if checked, the string resulting from the search must be null terminated. If not checked, the strings resulting from the search may or may not be null terminated.
- Pascal Strings - if checked, only strings that are valid pascal, pascal 255 or pascal unicode strings will be found.
- Word Model - specifies the Strings Analyzer model file used to detect high-confidence words. If this field is populated with a valid model file (default is 'StringModel.sng'), the resulting table will contain an "Is Word" column and an option to filter by whether the string is a word or not.
This field can be left blank and the word-related options will be omitted from the results table.
User-defined models should be placed in the Ghidra/Features/Base/data/stringngrams directory.
- Memory Block Types - Allows the user to specify if only loaded memory blocks should be searched for the strings, or all (unloaded + loaded).
- Selection Scope - Allows the user to specify if the entire address space should be searched or only the user selection.
- Search - press this button to find all strings using the current search options.
The results are displayed in tabular format. Strings can be created by selecting one or more rows from the resulting table and pressing the "Make String" button or ascii arrays with the "Make Ascii" button. An offset for the string(s) start can be specified to change the starting location(s) past the beginning of the string. String(s) can be automatically labeled.
- Defined - shows an icon that indicates the status of the string.
- indicates a string that has already been defined.
- indicates a string that is not defined.
- indicates a string that has been partially defined at some offset.
- indicates a string that conflicts with an instruction or some other data already defined at that address.
- Location - The address of the found string.
- Label - If one exists, the label at the location of the found string.
- Preview - If data or code already exists, the representation of that code or data. If no code or data exists, the undefined byte at the location of the found string.
- Ascii - What the string at the found location would look like if it were created.
- String Type - What type of string has been found. Currently, we support ascii strings, unicode strings, pascal strings, pascal 255 strings, and pascal unicode strings.
- Length - The number of characters in the string.
- Is Word - Whether the word model has determined, with high confidence, that the string is a valid word or sequence of words. NOTE: this table field is only available if the String Search Dialog 'Word Model' field contains a valid model file.
There are four toggle buttons in the table window's title bar that are used to control which strings are included in the table base on the strings "defined" state.
- toggles inclusion of defined strings.
- toggles inclusion of completely undefined strings.
- toggles inclusion of partially defined strings.
- toggles inclusion of strings that conflict with an instruction or some other data at the start address.
- toggles inclusion of high-confidence word strings. NOTE: this icon is only available if a String Search Dialog 'Word Model' field contains a valid model file.
- Make String - press this button to create either a string of the appropriate type (ascii or unicode) at the address(es) selected in the results table - if the option to automatically label is checked, a label will be placed at the beginning of the string(s).
- Make Char Array - press this button to create an array of chars at the address(es) selected in the results table - if the option to automatically label is checked, a label will be placed at the beginning of the char array.
- Offset - allows the user to specify a different starting point for the string or ascii array. The automatic label will reflect the changes in address and name. NOTE: This option is ignored for pascal strings because changing the offset would result in making the string an invalid pascal string.
- Auto Label - if checked, a label will be created when the string is created, that matches the string
- Include Alignment Nulls - if checked, strings will be created including any alignment nulls after the string, up to the alignment value.
- Truncate if Needed - if checked, a truncated string will be created if the string conflicts with an existing instruction or data that exists internal to the string. Otherwise, no string will be created if a conflict exists.
The "Make Strings" panel can be hidden/shown using the
/
toggle button at the end of the text filter.
Refresh
This action will cause the table to reload. The table attempts to keep the table up to date, but for efficiency reasons, not all external program changes will be accurately reflected in the strings table if those changes result in a conflict or partially defined string. A refresh will force the table to completely reload, resulting in accurate results.
Make Selection
See Make Selection.
Selection Navigation
See Selection Navigation.
Provided By: StringTablePlugin
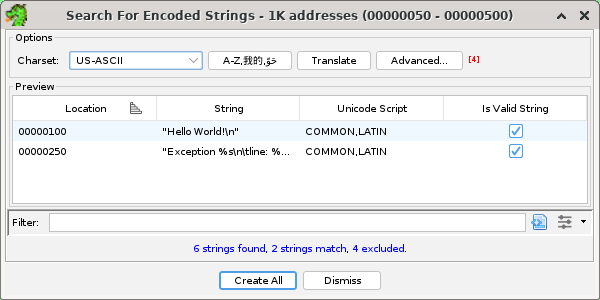
The Encoded Strings Dialog is an alternate way to find and create string instances in undefined data locations. It allows setting the character set (charset) of the string to be created, as well as the ability to filter out byte sequences from the selected locations that are not valid strings.
The Encoded Strings Dialog will initially allow the user to select the character set of the string to create, and displays a preview of the strings found in the current selection:
 |
Advanced options
Click the Advanced... and the A-Z,我的... (Filter by character scripts) buttons to show additional options that will allow filtering the selected byte range for strings containing specific scripts (alphabets) and also excluding strings that have properties that are unwanted.
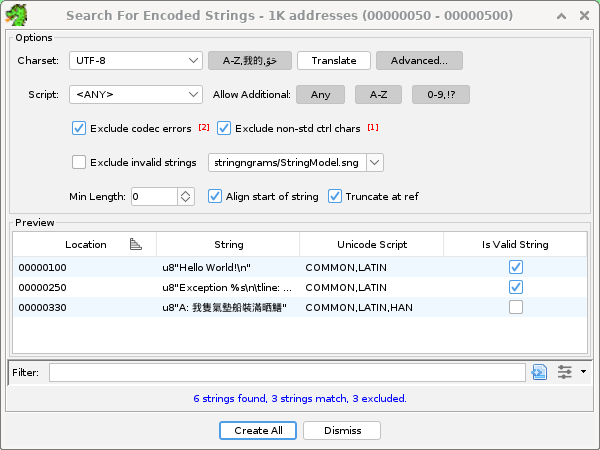 |
Character Script filtering
The Script drop-down list and the various Allow Additional toggle buttons control how strings are filtered based on the script (Latin, Cyrillic, Arabic, etc) of each of the characters found in the string.
The script chosen in the drop-down list will limit the included strings to strings that include at least one character of the desired script.
If no Allow Additional toggle buttons are pressed, included strings will be limited to strings that are solely comprised of characters from the chosen script (alphabet). This would exclude strings that contain characters such as the space character or numeric characters (labeled as the Common script), which typically is not desired. Select the 0-9,!? toggle to allow those characters.
The A-Z (Latin) toggle will allow Latin characters to be present in included strings. This is redundant if the Script drop-down list is already set to Latin, but becomes useful when another script is chosen, to allow including strings that are a mixture of the selected script and Latin, which commonly occurs when strings have symbol names, scientific units, etc.
The Any toggle will allow any additional script to be present in included strings.
More advanced filtering logic can be had by creating a column filter using Create Column Filter button in the lower right corner of the preview area and filtering on the Unicode Script column.
Exclude codec errors, non-standard control chars
The Exclude codec errors check box excludes strings that contain the Unicode REPLACEMENT character, which is placed into decoded strings when the charset codec logic encounters a byte or byte sequence that is invalid. For example, the US-ASCII charset will translate bytes greater than 0x7f into REPLACEMENT characters.
The Exclude non-std ctrl chars check box excludes strings that contain characters that correspond to control characters in the range 1..31, but ignoring common control characters such as tab, CR, LF.
Exclude invalid strings
The Exclude invalid strings option tests each candidate string against a pre-built trigram frequency model and rejects strings that score lower than a cut-off value.
The built-in string model file was trained with mostly english strings, and will probably mark valid words from other languages as invalid.
Misc options
Minimum Length - excludes strings shorter than this (measured in characters, not bytes)
Align start of string - ensures strings start at a location that is evenly divisible by the alignment requirements of the character size of the charset.
Truncate at ref - ends strings early when there is an inbound reference to a character inside the string.
Tip
When an option is responsible for excluding / filtering-out a string, that option will have a red superscripted number next to it that contains the total count of strings excluded by that option.
Related
See the Defined Strings window to see already created strings.
Provided By: EncodedStringsPlugin